NoiseCapture calibration
NoiseCapture calibration
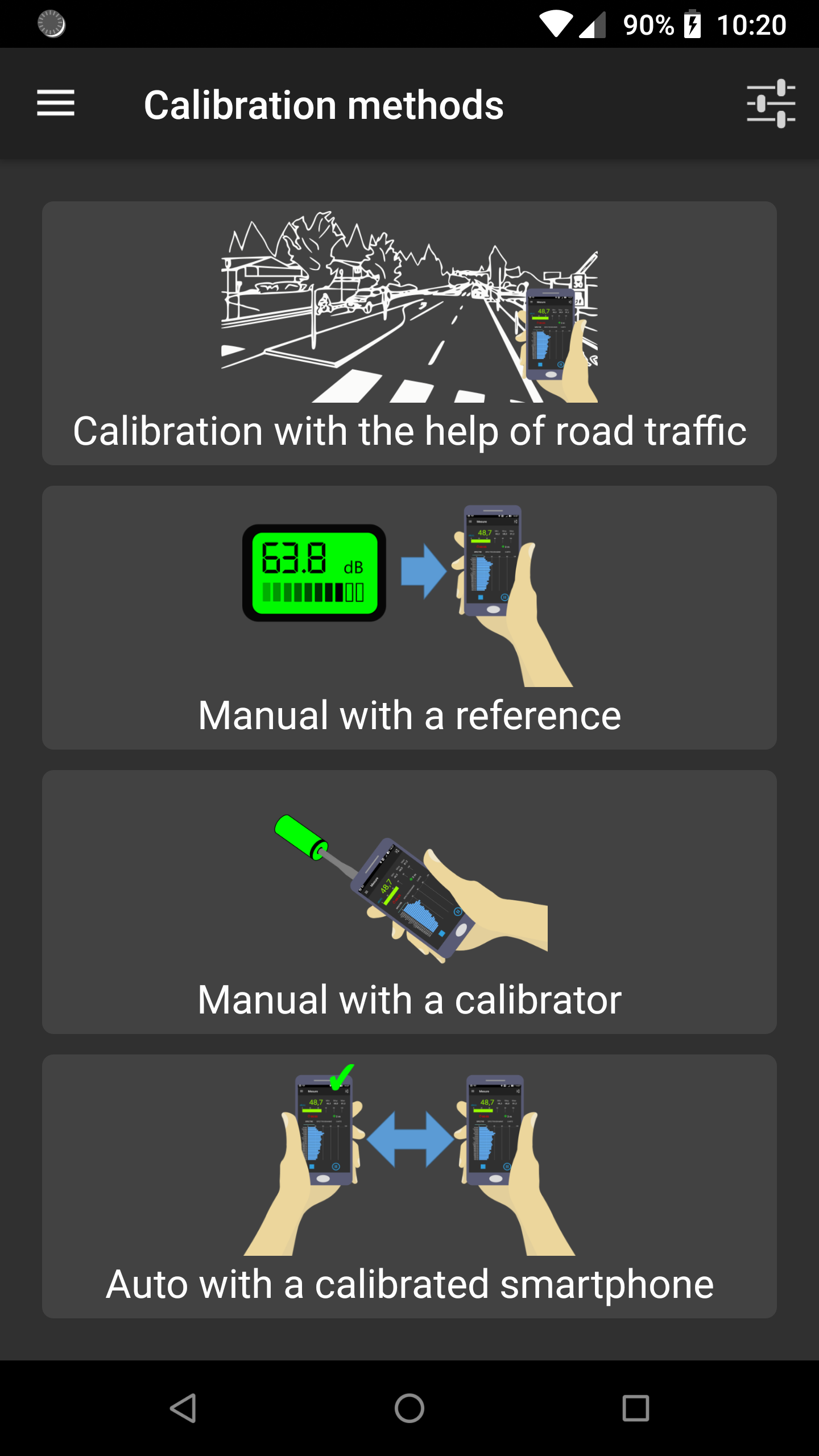
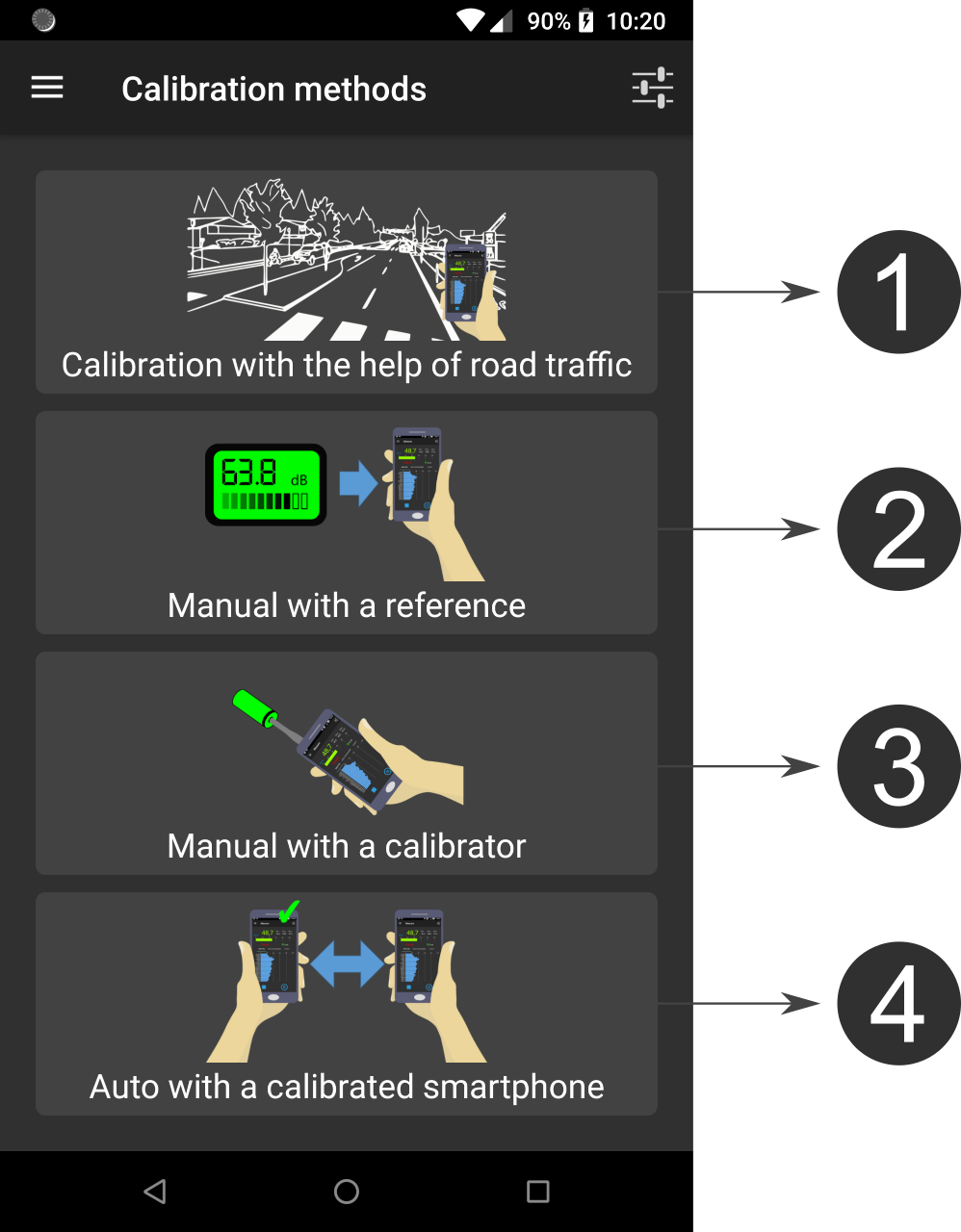
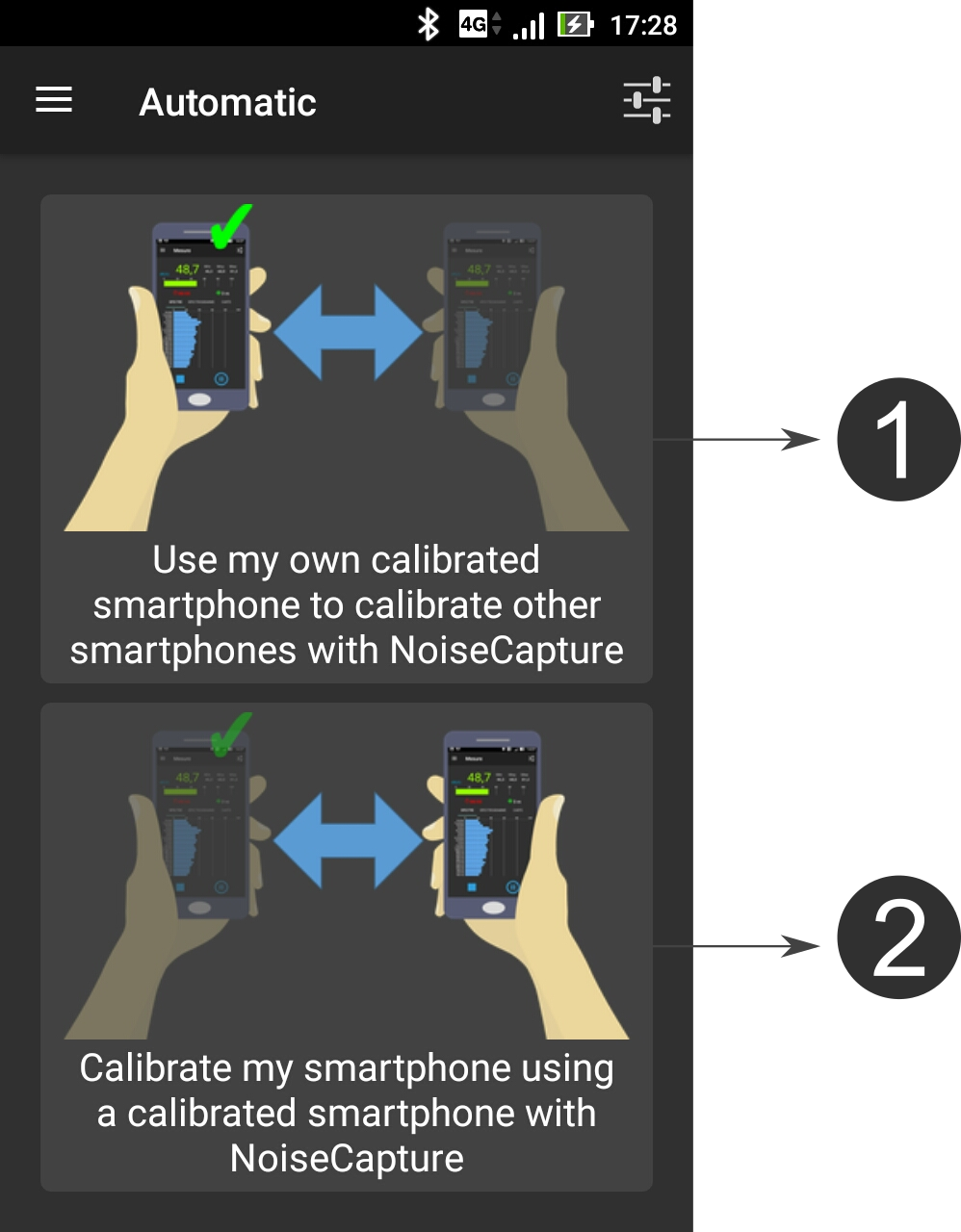
On the Calibration menu item, users have the opportunity to calibrate their smartphone.
The smartphone calibration is a crucial and recommanded step. Without calibration, you can be sure that the measured data will be wrong!
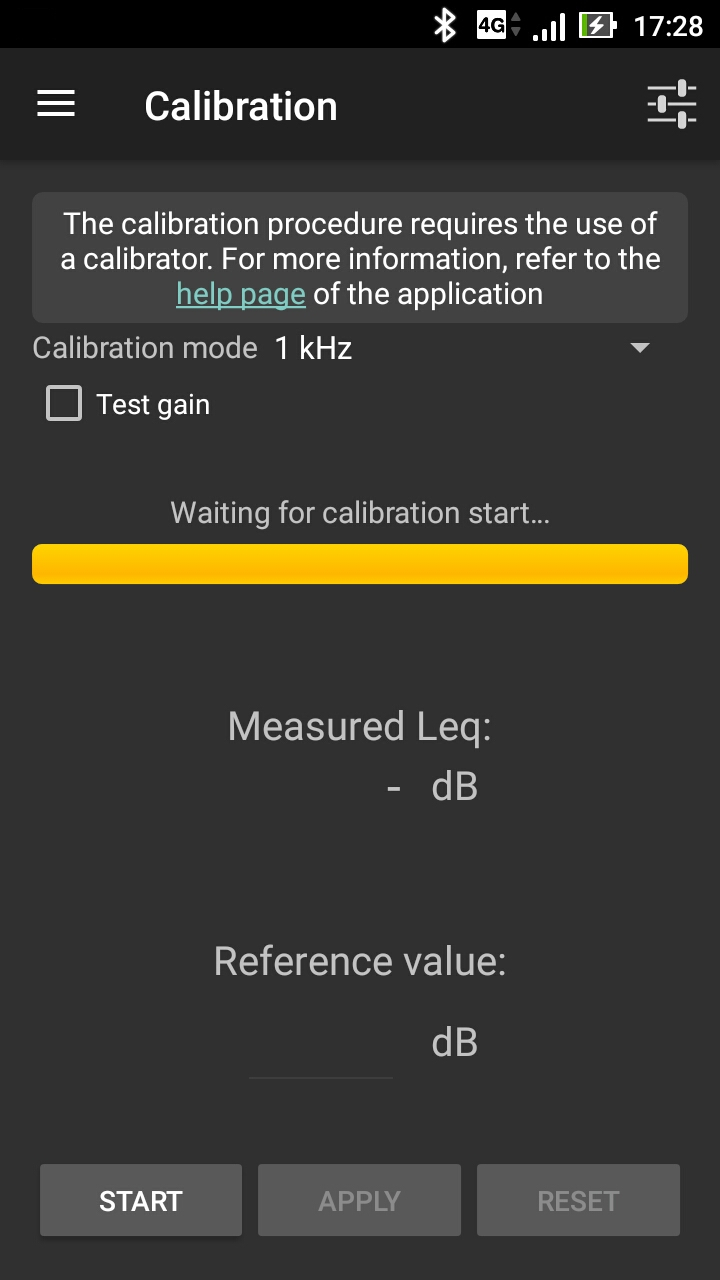
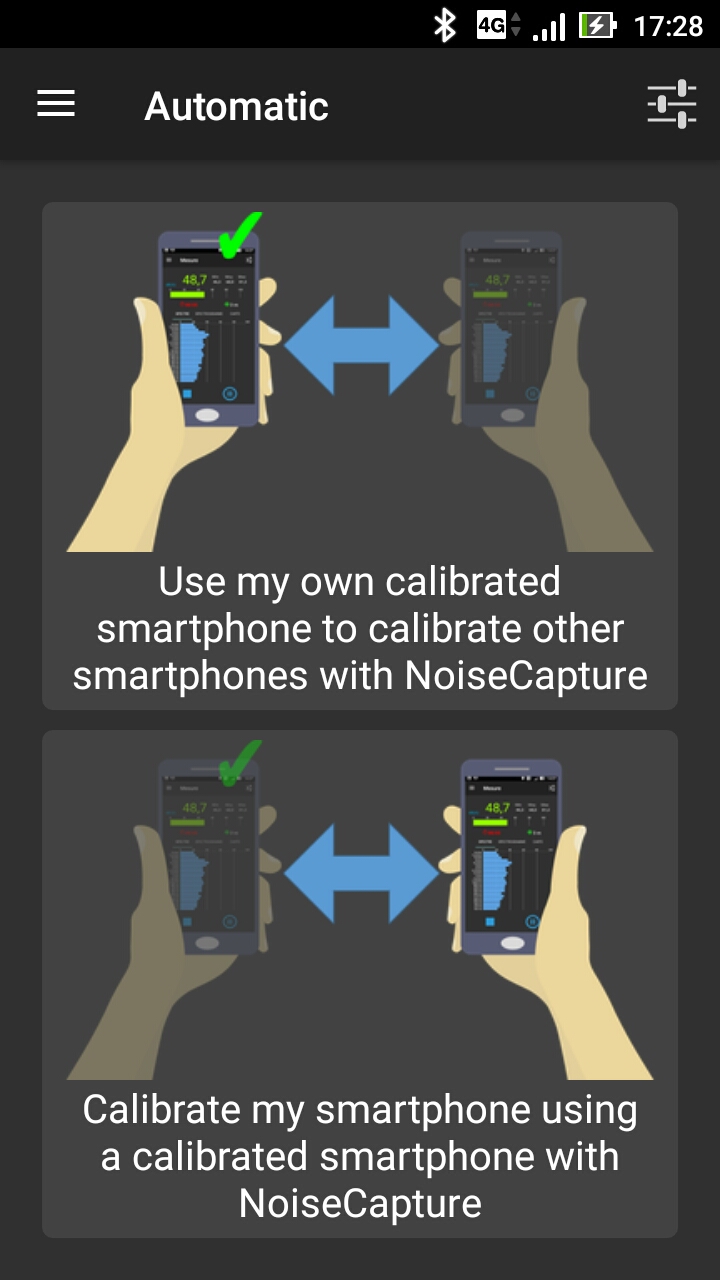
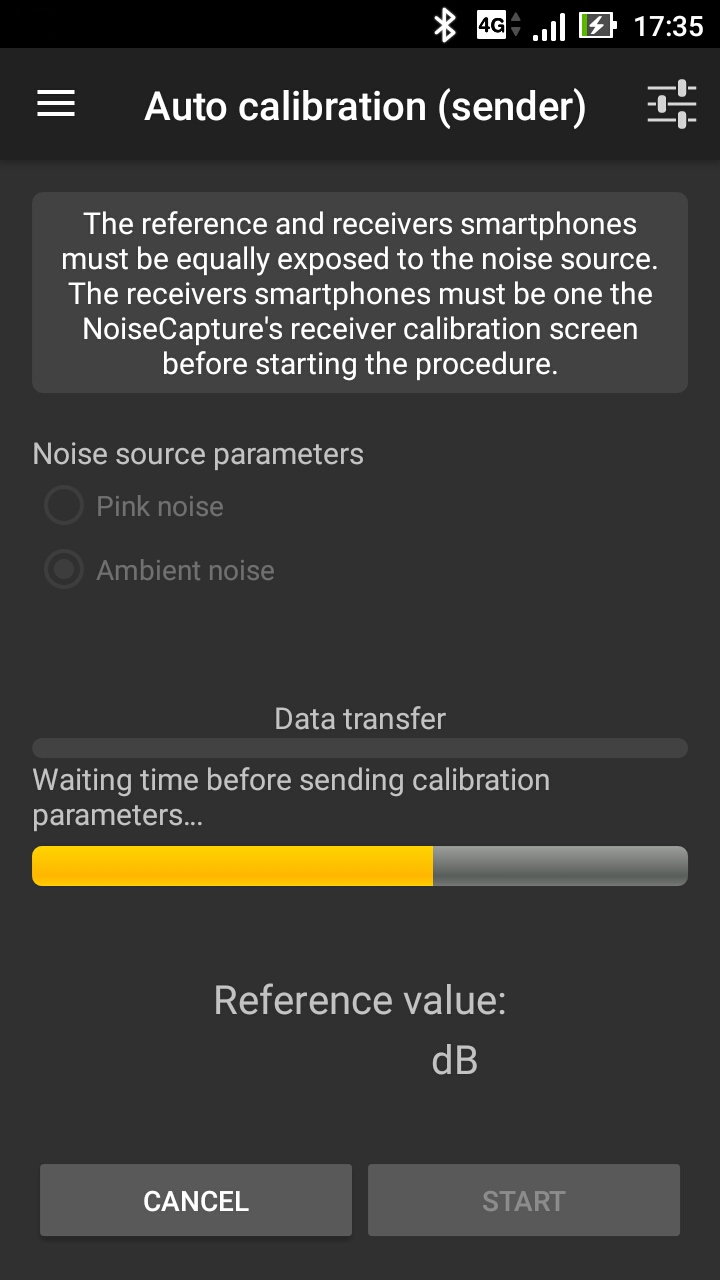
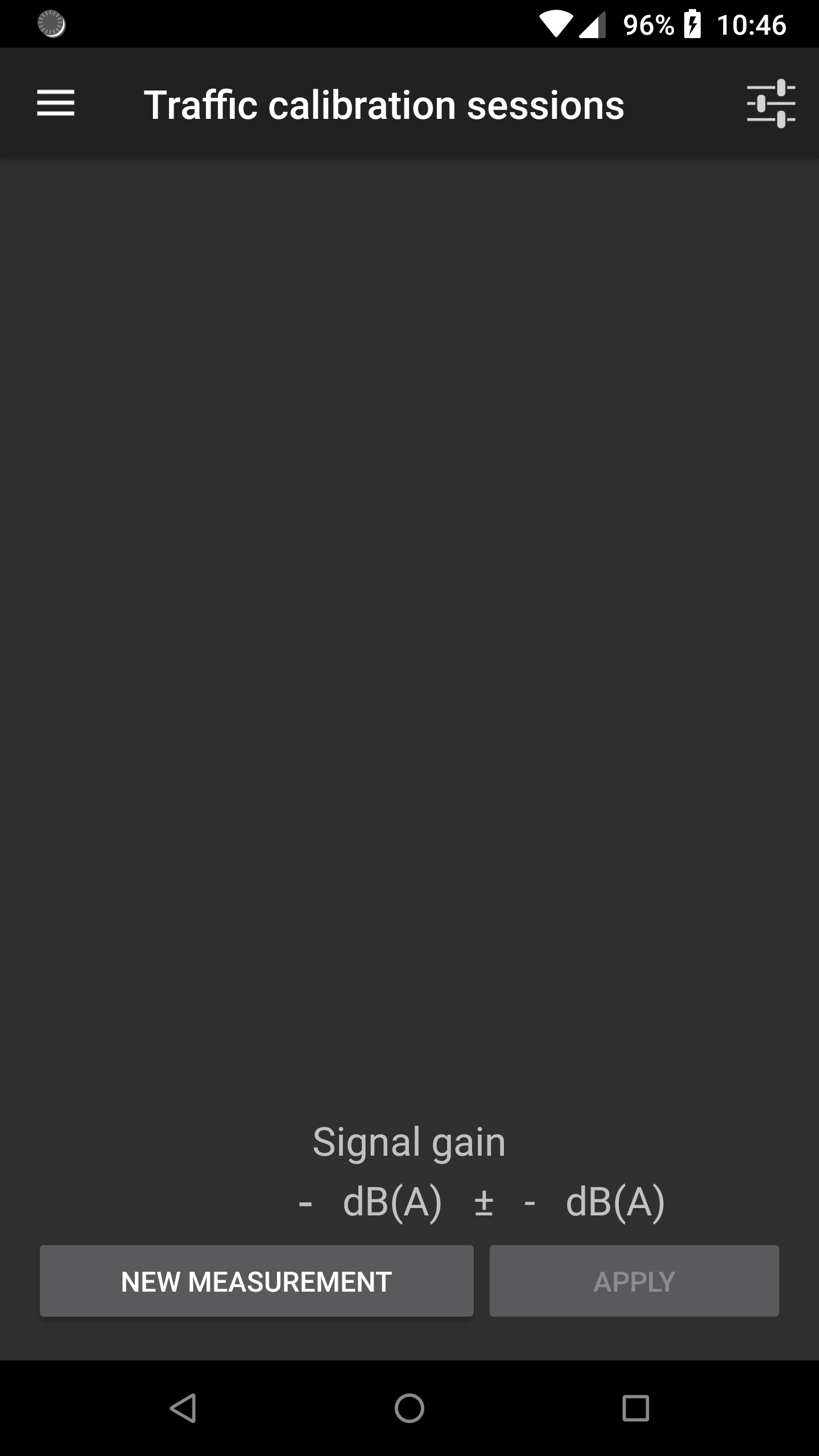
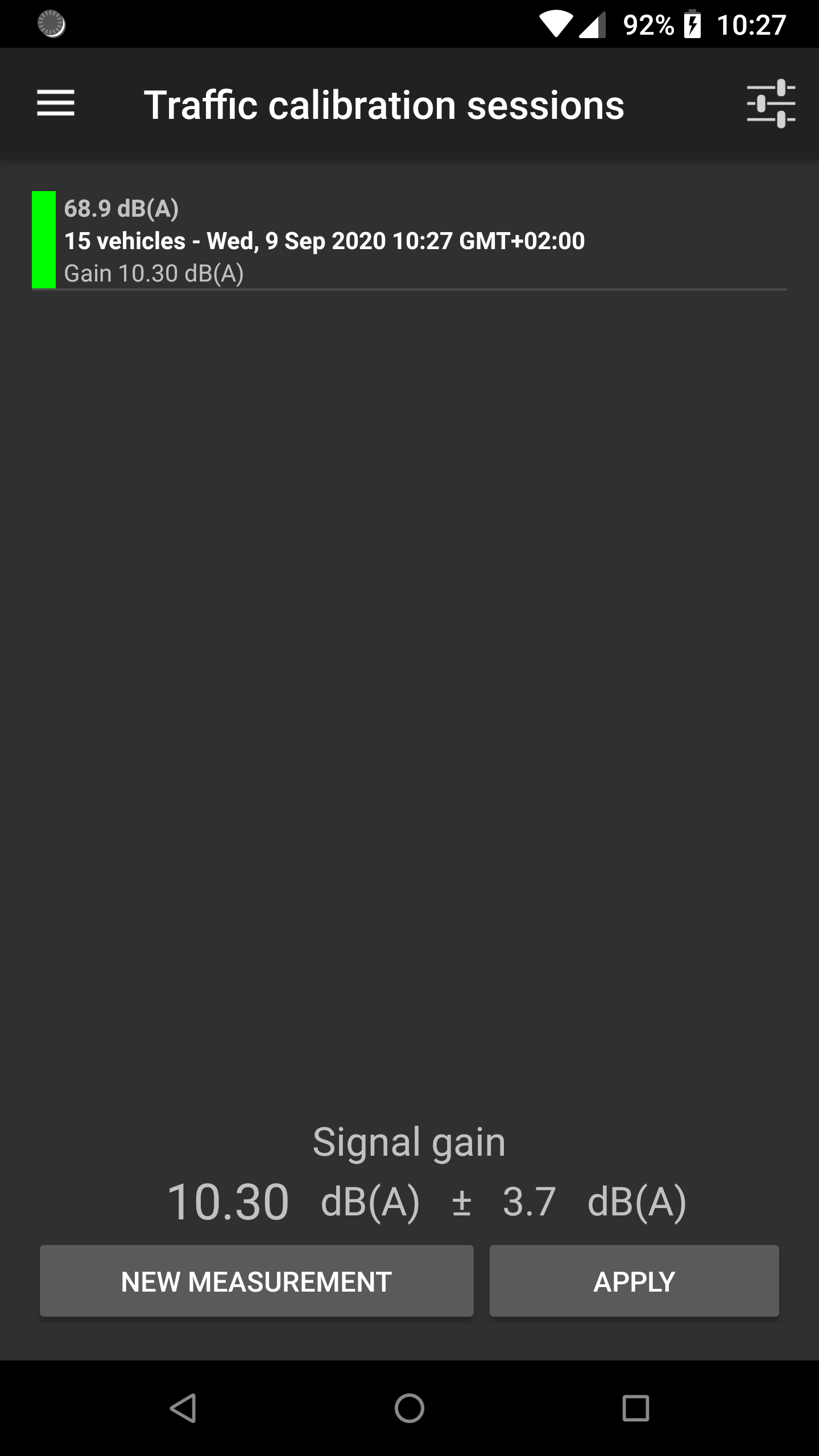
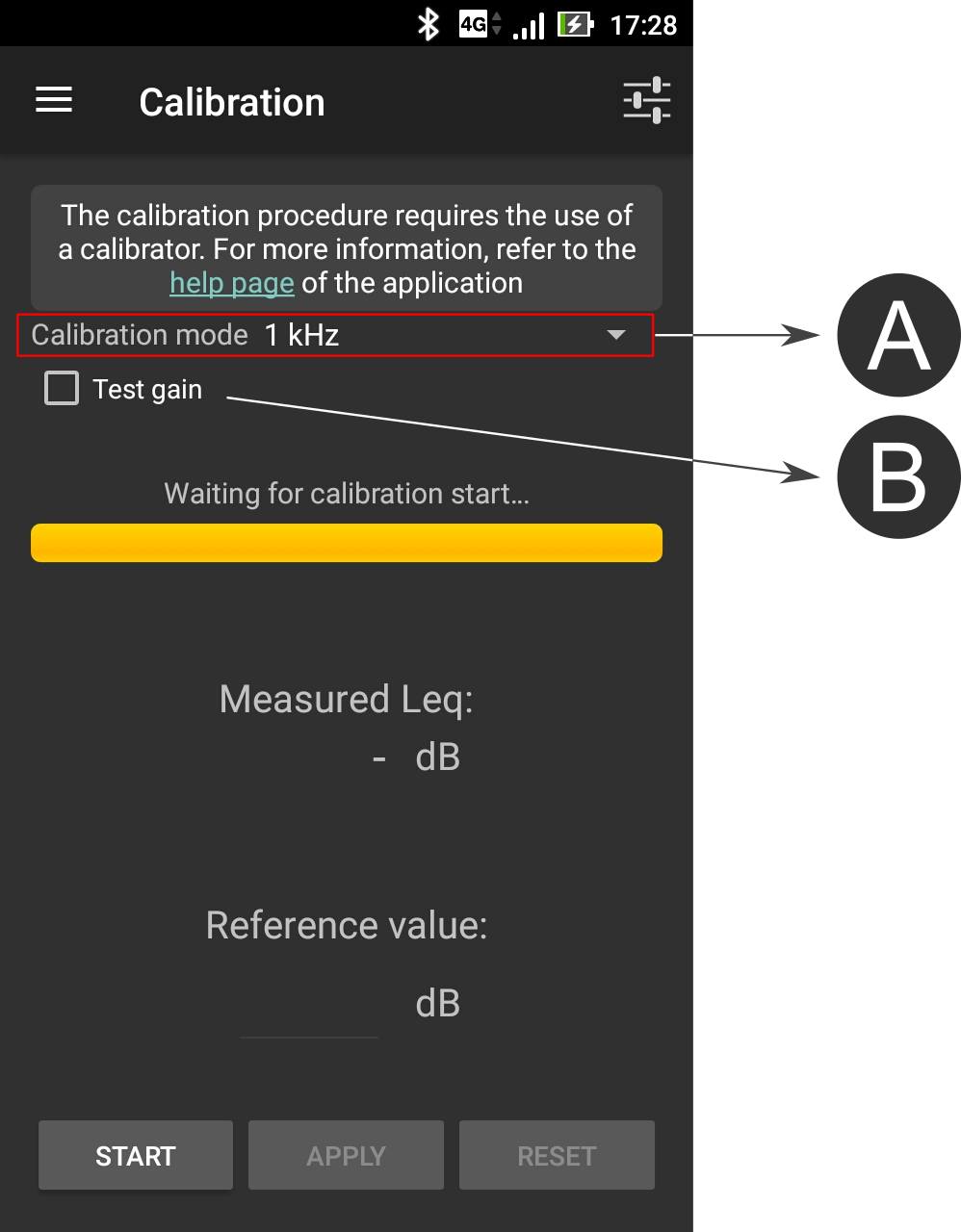
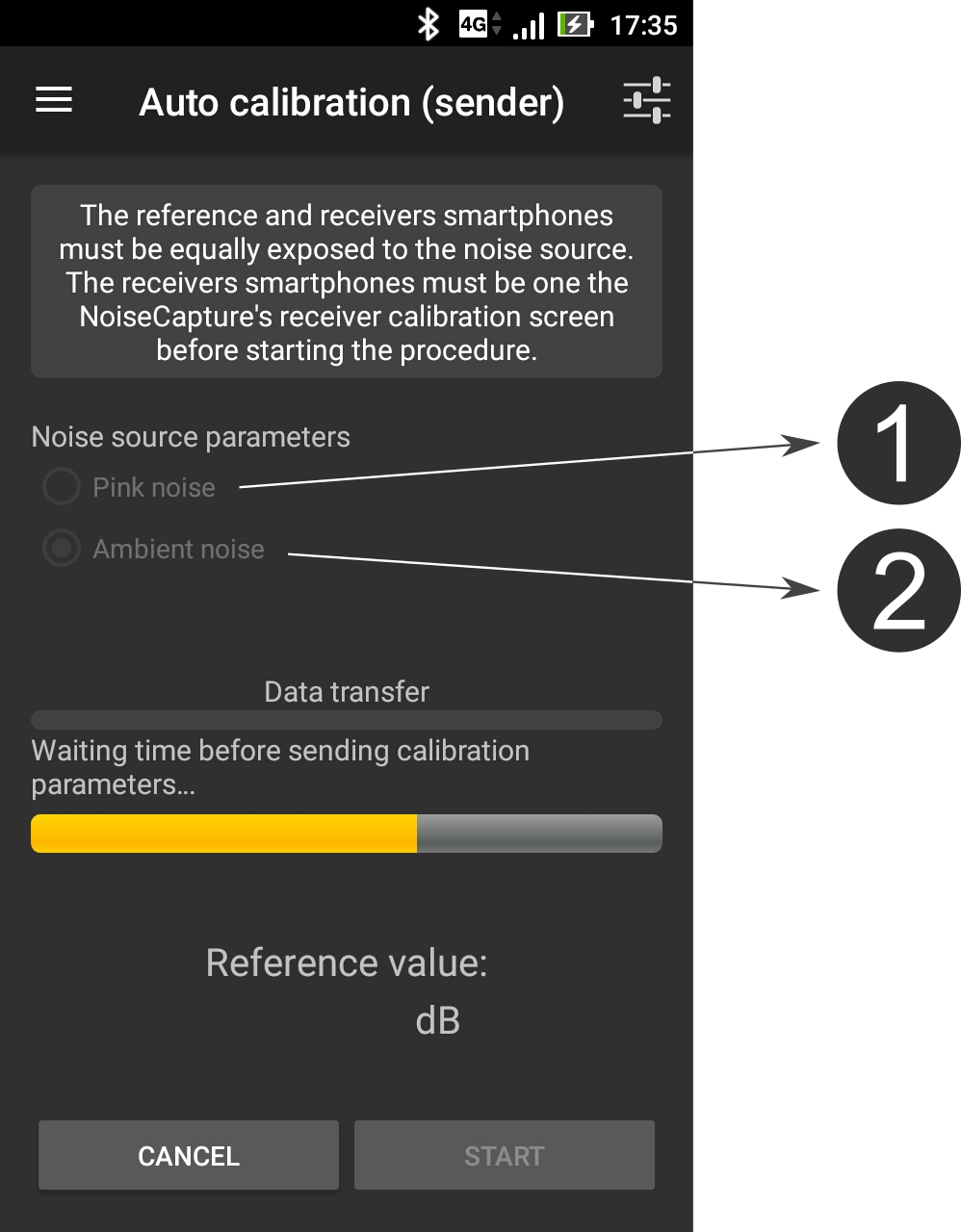
The methodology is based on the knowledge of a Reference value for the equivalent noise level Leq (in dB, not in dB(A)) for a given duration, from a reference device (an acoustic calibrator, a calibrated smartphone, a sound level meter). Depending on the calibration method, the calibration can be performed for a given frequency band or for the full range (global value). This Reference value is then compared to the Measured Leq (in dB) using the smartphone. The difference between these two values gives a correction factor (i.e. the signal gain) that will be applied to the input signal.
Warning:
- The correction factor is applied for the whole signal. Multi-frequency calibration is not possible for now.
- The calibration is carried out with dB values, not dB(A).